[텐서플로우로 시작하는 딥러닝 기초] Lab 02: Simple Linear Regression 를 TensorFlow 로 구현하기
2020. 8. 4. 22:55ㆍ머신러닝
import tensorflow as tf
x_data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y_data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
W = tf.Variable(2.9)
b = tf.Variable(0.5)
# hypothesis = W*x+b
hypothesis = W*x_data+b
#cost(W,b)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - y_data))
reduce_mean 은 평균을 내는 함수인데 reduce는 차원의 감소를 의미한다.
cost를 최소화 하는 알고리즘 중 Gradient descent는 경사를 줄이면서 cost가 minimize되는 W와 b를 찾는다.
우리의 데이터를 보아 W값은 1, b값은 0에 가까운 값이 나와야 할 것이다.
# Learning_rate initialize
learning_rate = 0.01
# Gradient descent
# tape에 hypothesis와 cost의 값을 기록해나간다.
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
hypothesis = W*x_data+b
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - y_data))
# W_grad, b_grad에 각각 cost 함수에서 W와 b에 대한 미분값을 넣는다.
W_grad, b_grad = tape.gradient(cost, [W, b])
W.assign_sub(learning_rate * W_grad)
b.assign_sub(learning_rate * b_grad)A.assign_sub(b) 는 A에 b를 뺀 값을 다시 할당하는 명령어. (A -= B를 Tensorflow에서는 못쓰기 때문)
위의 코드가 한 번의 학습. Epoch=1이고 이를 반복하여 점점 cost가 줄어드는 모습을 확인해보자.
full code :
import tensorflow as tf
x_data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y_data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
W = tf.Variable(2.9)
b = tf.Variable(0.5)
# hypothesis = W*x+b
hypothesis = W*x_data+b
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - y_data))
# Learning_rate initialize
learning_rate = 0.01
for i in range(101):
# Gradient descent
# tape에 hypothesis와 cost의 값을 기록해나간다.
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
hypothesis = W*x_data+b
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - y_data))
# W_grad, b_grad에 각각 cost 함수에서 W와 b에 대한 미분값을 넣는다.
W_grad, b_grad = tape.gradient(cost, [W, b])
W.assign_sub(learning_rate * W_grad)
b.assign_sub(learning_rate*b_grad)
if i % 10 == 0:
print("{:5}|{:10.4f}|{:10.4}|{:10.6f}".format(i, W.numpy(), b.numpy(), cost))
출력 :
10| 1.1036| 0.0034| 0.206336
20| 1.0128| -0.0209| 0.001026
30| 1.0065| -0.0218| 0.000093
40| 1.0059| -0.0212| 0.000083
50| 1.0057| -0.0205| 0.000077
60| 1.0055| -0.0198| 0.000072
70| 1.0053| -0.0192| 0.000067
80| 1.0051| -0.0185| 0.000063
90| 1.0050| -0.0179| 0.000059
100| 1.0048| -0.0173| 0.000055
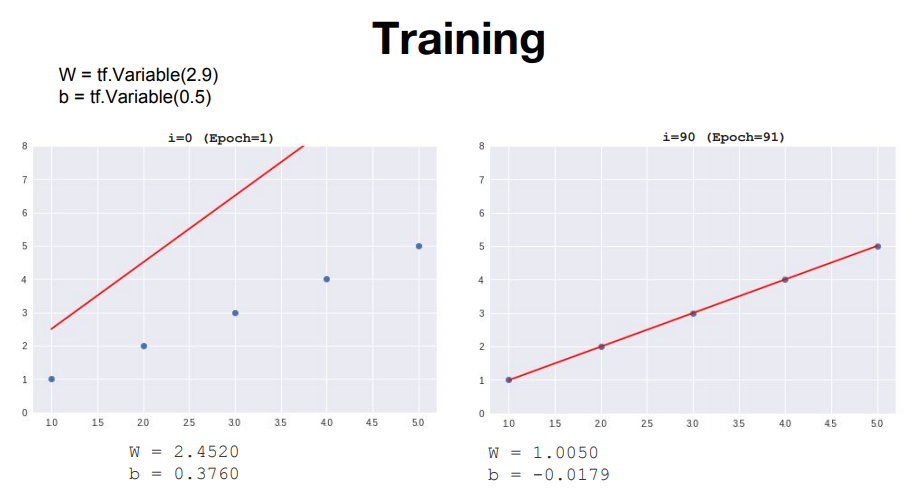
cost가 0에 근접하고 W와 b의 값 또한 예상에 매우 근접하는 모습을 볼 수 있다. 다음 강의에서는 이 Gradiant descent 알고리즘에 대해 자세히 알아 보겠다.
'머신러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [텐서플로우로 시작하는 딥러닝 기초] Lab 03: Linear Regression and How to minimize cost 를 TensorFlow 로 구현하기 (0) | 2020.08.09 |
|---|---|
| [텐서플로우로 시작하는 딥러닝 기초] Lec 03: Linear Regression and How to minimize cost (0) | 2020.08.05 |
| [텐서플로우로 시작하는 딥러닝 기초] Lec 02: Simple Linear Regression (0) | 2020.08.04 |
| [OSAM] 2. Training set과 Test set, Overfitting과 Underfitting (0) | 2020.08.03 |
| [OSAM] 1. 머신러닝의 개념 (OT) (0) | 2020.08.03 |